What is CNC Machining?
Introduction
In the world of manufacturing and engineering, CNC machining stands out as a transformative technology that has revolutionized the way products are designed and produced. But what exactly is CNC machining, and why is it so important? This guide will explore the fundamentals of CNC machining, its applications, benefits, and the role it plays in modern industry.
Understanding CNC Machining
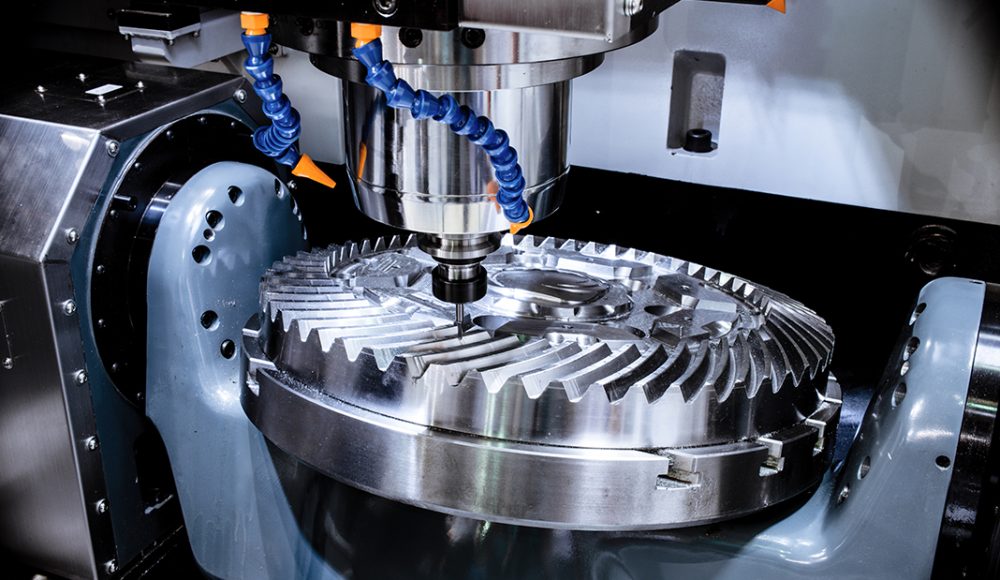
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. CNC machining is a manufacturing process in which pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This process can control a range of complex machinery, from grinders and lathes to mills and routers. With CNC machining, three-dimensional cutting tasks can be accomplished in a single set of prompts.
How CNC Machining Works
Design Creation:
The process begins with a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model, which is a detailed 3D representation of the final product. This model is then translated into a CNC program that guides the machine.
Programming:
The CAD model is converted into a CNC program using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. This program contains the instructions for the machine to follow, including tool paths, speeds, and feed rates.
Machine Setup:
The CNC machine is set up with the necessary tools and materials. The machine’s axes are calibrated to ensure precision.
Machining Process:
Once the machine is set up, the CNC program is executed, and the machine begins the cutting process. The machine follows the programmed instructions to create the desired shape from the material.
Quality Control:
After machining, the part is inspected for accuracy and quality. Any necessary adjustments are made to ensure the final product meets the required specifications.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is used across various industries, including:
Aerospace: For creating high-precision components such as engine parts and structural elements.
Automotive: In the production of complex parts like gears, shafts, and engine components.
Medical: For manufacturing surgical instruments and implants with high accuracy.
Electronics: In the production of intricate parts for devices and circuit boards.
Benefits of CNC Machining
Precision and Accuracy: CNC machines can produce complex shapes with high precision and repeatability.
Efficiency: CNC machines can operate continuously, reducing production times and increasing output.
Flexibility: With the ability to quickly change programs, CNC machining can accommodate a wide range of designs and materials.
Safety: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, minimizing the risk of accidents.
Challenges and Considerations
While CNC machining offers numerous advantages, it requires significant investment in machinery and software. Skilled operators are also needed to program and maintain the machines. Additionally, the complexity of CNC programming can be a barrier for some manufacturers.